Role in Urban and Rural Planning and Development
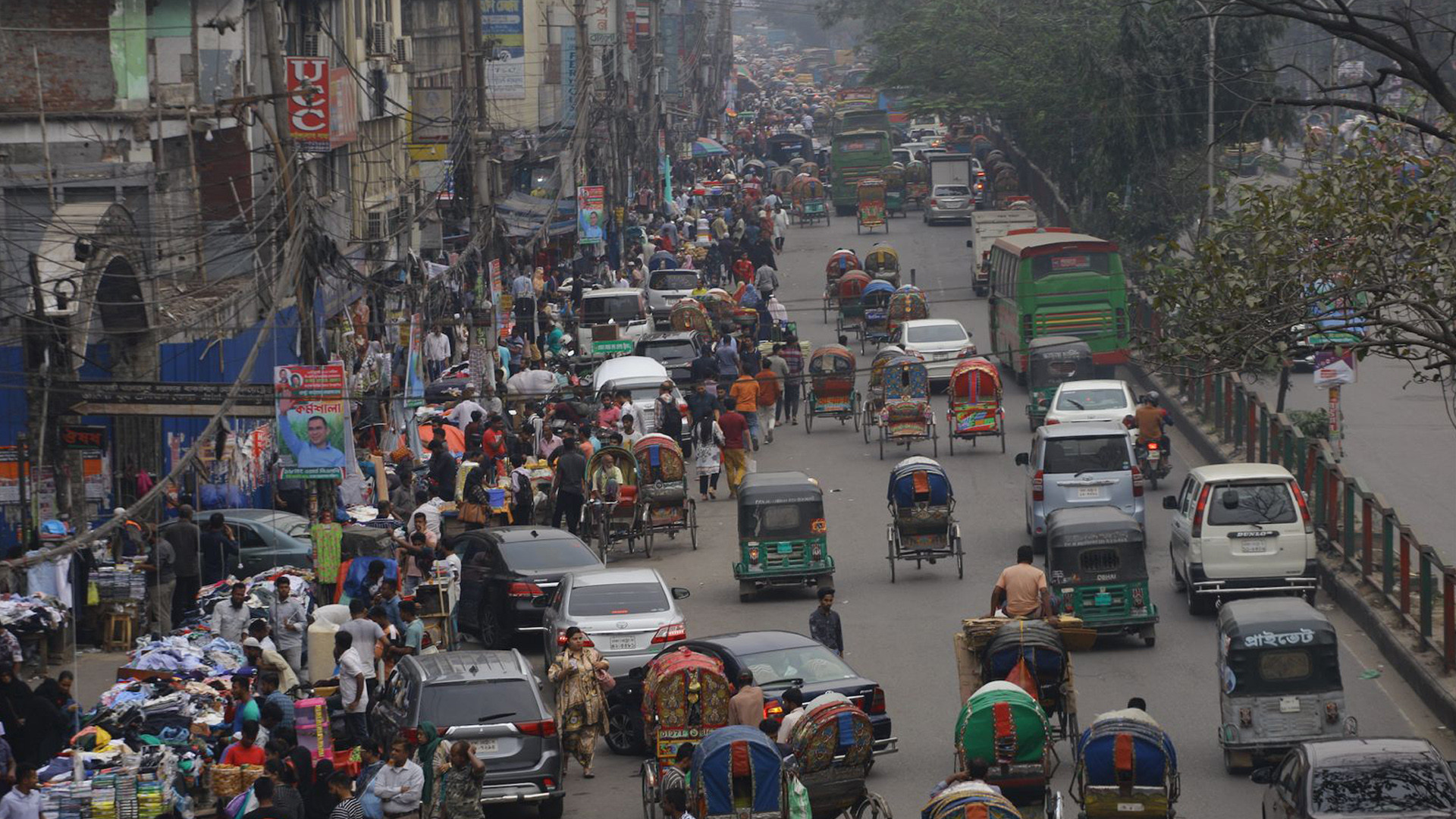
Platform Bangladesh envisions a balanced development model that simultaneously addresses the pressing challenges of urban overcrowding and rural underdevelopment. In urban areas, the focus is on improving infrastructure, public health, mobility, and environmental sustainability. Key initiatives include upgrading footpaths for accessibility, introducing smart traffic systems, managing waste through segregation and smart bins, and enhancing public utilities like drinking water kiosks and air-purifying booths. The plan also promotes green spaces, cycle-friendly transport, noise control, and modular low-cost housing for service workers, aiming to create healthier, more livable cities.
In rural regions, the strategy targets housing resilience, energy access, market connectivity, and climate adaptation. Cyclone-resistant homes, solar microgrids, organic farming support, and digital platforms for direct farmer-to-consumer sales are among the core interventions. These efforts are complemented by artisan hubs, improved sanitation, and robust flood management systems to uplift livelihoods and build resilience.
The implementation framework includes the formation of Urban-Rural Development Committees (URDCs), funding through public-private partnerships and micro-financing, and the use of technology like GIS mapping and mobile platforms for effective monitoring. Rolled out in three phases—Pilot, Scale, and Optimize—this initiative aims to create jobs, enhance public health, protect the environment, and position Bangladesh as a leader in inclusive and sustainable development.
Urban Development
- Footpath Improvement
- Garbage Management
- Cleaning Initiatives
- Prevention of Mosquito Breeding
- Pure Drinking Water Management
- Pure Breath Booths for Asthma Patients
- Seating, Benches, and Street Furniture
- Internet and Cable Management
- Traffic Control and Lane Management
- Dedicated Lanes for Cycles and Rickshaws
- Green Plantation
- Protecting Trees beside Lakes
- Maintenance of Trees and Street Signage
- Low-Cost Housing for Service Workers
- Public Toilets
- Traffic Police Positioning
- Noise Control
- Green Spaces and Public Health
- Fix the Road Level
Rural Development
- Rural Housing
- Compact Housing Solutions
- Tree Plantation Initiatives
- Craft Work Job Facilities
- Organic Food Production
- Direct Farmer-to-Consumer Sales
- Sustainable Energy Use
- Proper Sanitation
- Emergency Flood Management
Our Role in Urban and Rural Planning and Development:
Our Role in Urban and Rural Planning and Development
Urban centers in Bangladesh face challenges of overpopulation, traffic congestion, public health concerns, and infrastructure deficits. The following proposals aim to alleviate these issues through integrated and community-focused solutions:
1. Footpath Improvement:
Upgrade and widen footpaths to ensure pedestrian safety. Include tactile paving for the visually impaired and ramps for the differently-abled. Partner with municipalities to enforce encroachment-free sidewalks.
2. Garbage Management:
Implement a three-bin waste segregation system (organic, recyclable, landfill) and partner with waste-to-energy plants. Regular training and equipment support for municipal workers are essential.
3. Cleaning Initiatives:
Daily street sweeping and monthly community clean-up drives supported by NGOs, volunteers, and local authorities. Smart bins with fill-level sensors can automate collection schedules.
4. Prevention of Mosquito Breeding:
Deploy regular fogging, larvicide treatment, and public awareness drives on stagnant water. Integrate real-time mosquito mapping using IoT sensors.
5. Pure Drinking Water Management:
Establish community water filtration kiosks in densely populated areas. Use mobile water testing units to monitor contamination levels.
6. Pure Breath Booths for Asthma Patients:
Install air-purifying stations equipped with HEPA filters in high-traffic zones. Partner with local health NGOs for awareness campaigns on air quality.
7. Seating, Benches, and Street Furniture:
Design shaded, ergonomic public benches using recycled materials. Street furniture must include solar-powered charging stations and public information kiosks.
8. Internet and Cable Management:
Organize overhead cables into underground ducts. Facilitate Wi-Fi hotspots in major public squares for equitable internet access.
9. Traffic Control and Lane Management:
Introduce smart traffic lights, integrated surveillance, and AI-based congestion prediction tools. Separate lanes for commercial and private vehicles.
10. Dedicated Lanes for Cycles and Rickshaws:
Promote eco-friendly transport by demarcating cycle/rickshaw lanes with physical barriers. Offer incentives for non-motorized vehicle use.
11. Green Plantation:
Launch a "One Citizen, One Tree" campaign. Green rooftops and vertical gardens for heat reduction in urban heat islands.
12. Protecting Trees beside Lakes:
Legal protection for urban green zones. Create buffer zones around water bodies with native plant species to preserve ecosystems.
13. Maintenance of Trees and Street Signage:
Digitize tree tagging for monitoring health and age. LED-based street signage for visibility and energy efficiency.
14. Low-Cost Housing for Service Workers:
Develop modular housing using prefabricated materials near city centers. Collaborate with micro-financing institutions for affordability.
15. Public Toilets:
Construct gender-segregated, wheelchair-accessible toilets at 1 km intervals. Employ smart sensors for cleanliness and maintenance tracking.
16. Traffic Police Positioning:
Equip officers with GPS-linked apps for better coordination. AI surveillance tools to support law enforcement during peak hours.
17. Noise Control:
Use noise barriers in critical zones and strict decibel monitoring near hospitals and schools. Penalize illegal horn usage.
18. Green Spaces and Public Health:
Design urban parks with walking tracks, exercise equipment, and meditation zones. Partner with health startups for wellness kiosks.
19. Fix the Road Level:
Use drone-based topography mapping to identify uneven roads. Rapid asphalt mix tech for quick and durable road patching.
Rural Development Planning Options
Rural areas of Bangladesh face challenges such as poor sanitation, lack of energy access, limited market connectivity, and climate vulnerabilities. These interventions aim to improve livelihoods and build climate resilience:
1. Rural Housing:
Introduce cyclone-resistant housing with local materials. Integrate community halls and shared amenities in each housing cluster.
2. Compact Housing Solutions:
Pilot vertical living models in semi-urban rural belts to preserve agricultural land while enhancing living standards.
3. Tree Plantation Initiatives:
Mass plantation drives with farmer incentives. Focus on fruit-bearing and timber trees for added economic value.
4. Craft Work Job Facilities:
Develop rural artisan hubs with tools, training, and export market linkages. Promote traditional crafts through e-commerce platforms.
5. Organic Food Production:
Support organic input distribution centers and certification labs. Facilitate farm cooperatives to standardize practices and negotiate better prices.
6. Direct Farmer-to-Consumer Sales:
Launch digital platforms and weekly haat bazaars where farmers can sell produce directly. Implement a farm-to-table logistics chain using electric vans.
7. Sustainable Energy Use:
Promote solar microgrids, clean cookstoves, and bio-digesters. Provide subsidies and community training for maintenance.
8. Proper Sanitation:
Build low-cost, twin-pit toilets in villages with piped water connections. Launch awareness campaigns around hygiene and menstrual health.
9. Emergency Flood Management:
Establish community-based flood early warning systems. Raise embankments, create water retention basins, and train local rescue teams.
Implementation Framework
- Governance: Form local Urban-Rural Development Committees (URDCs) under district administrations.
- Funding: Leverage public-private partnerships (PPPs), foreign aid, CSR funds, and micro-financing.
- Technology: Use data analytics, mobile platforms, and GIS mapping for monitoring and feedback.
- Sustainability: Prioritize environment-friendly materials, circular economy models, and inclusive planning processes.
- Timeline: Roll out the plan in three phases—Pilot (Year 1), Scale (Years 2–3), and Optimize (Year 4 onward).
Conclusion
Platform Bangladesh envisions a new era of development where urban modernization and rural uplift go hand in hand. This proposal, if implemented, will create jobs, boost health outcomes, protect the environment, and make Bangladesh a model of balanced development.